FAT32 Vs NTFS: Picking The Right File System For Your Drives Today
Choosing the right way to set up your storage can feel a bit like picking the right tool for a job. When you are reformatting a drive, memory card, or flash drive, you need to pick a file format. You might see options like FAT32, exFAT, and NTFS, and honestly, figuring out which one to pick can be a bit puzzling for many folks.
It's a common moment for computer users, especially when getting a new USB stick or an external hard drive. This choice matters because it affects how your stuff is stored, how big your files can be, and what devices will even be able to read your drive. So, getting a basic understanding of NTFS and FAT32 is pretty helpful.
This detailed article will explore FAT32 and NTFS in depth. We'll look at their good points and their weak points to help you decide which file system might be the best fit for your needs right now, in 2024. After all, you want your storage to work just right, you know?
Table of Contents
- What Exactly Are File Systems?
- FAT32 vs NTFS: The Big Differences
- When to Pick Which: Use Cases
- Formatting Your Drive: A Quick Guide
- Frequently Asked Questions About File Systems
What Exactly Are File Systems?
Imagine a big library. A file system is kind of like the librarian, deciding where every book goes, how it's labeled, and how you find it later. It's the way your computer organizes and manages files on storage devices. This includes things like hard drives, USB flash drives, and memory cards, which is pretty important for everything to run smoothly. Without one, your computer would just see a jumble of bits and bytes, which wouldn't be very helpful.
Both NTFS and FAT file systems are used in an operating system, but they handle things in different ways. Each of the three FAT file systems—FAT12, FAT16, and FAT32—has a different file size and disc layout, for example. So, you know, it's not just one size fits all, apparently.
A Quick Look at FAT32
FAT32, short for File Allocation Table 32, has been around for a while. Microsoft introduced it back in 1996, and it remains one of the most universally compatible file systems. This format still matters quite a bit, even today, because it's perfect for ensuring compatibility with various devices, which is a big plus.
Formatting your USB flash drive using the FAT32 file system is as easy as selecting a few options or running a command on your Windows 11 or Windows 10 PC. There's even a free program called Fat32format that enables people to configure any hard drive, micro SD card, SD card, and USB drive that is more than 32 GB to the FAT32 file system. Fat32format is a portable freeware utility capable of formatting large USB drives (32 GB+) to FAT32, which is really handy.
Getting to Know NTFS
NTFS stands for New Technology File System. It's the default file system for modern Windows versions, and it's packed with modern features that FAT32 and even exFAT don't have. This means it can handle a lot more than its older sibling, in a way.
NTFS supports large file and volume sizes, which is a big deal for today's huge files and drives. It also provides efficient data organization compared to FAT. Plus, it offers different enhancements and increased security, which is a pretty good thing for protecting your stuff. For instance, NTFS supports file permissions for security, and it has a change journal that can help quickly recover errors if something goes wrong, you know?
FAT32 vs NTFS: The Big Differences
After getting a basic understanding of NTFS and FAT32, now you can look into their differences in speed, file size limit, compatibility, and other things. These distinctions are what really guide your choice when you're setting up a new drive. It's not just about one being "better" than the other; it's about what works best for your specific situation, really.
File Size and Volume Limits
This is probably the most talked-about difference. FAT32 has a pretty famous limit: a single file cannot be larger than 4 GB. This means if you have a movie file or a big game installer that's bigger than 4 GB, you simply can't put it on a FAT32 drive. Also, a FAT32 partition itself can't be larger than 2 TB, which is a bit restrictive for today's massive hard drives, you know?
NTFS, on the other hand, handles much larger files and volumes. We're talking about theoretical limits that are so big, you probably won't hit them with current technology. This makes NTFS the go-to choice for internal hard drives and large external drives where you might store very big files, like high-definition videos or extensive software backups. So, it's definitely got more room to grow, apparently.
Device Compatibility
FAT32's age is actually its strength here. Because it's been around for so long, nearly every operating system and device can read and write to a FAT32 drive. This includes Windows, macOS, Linux, game consoles (like PlayStation and Xbox), smart TVs, and many other media players. It's incredibly versatile, which is a huge plus for sharing things between different gadgets, more or less.
NTFS is primarily a Windows file system. While macOS can usually read NTFS drives, it often can't write to them without extra software. Linux systems can typically read and write to NTFS, but it sometimes requires a bit of setup. Game consoles and other consumer electronics generally don't support NTFS, which limits its use for universal sharing. So, for broad compatibility, FAT32 usually wins, you know, for a lot of devices.
Security and Permissions
Here's where NTFS really shines. It's packed with modern features not available to FAT32. One big one is file permissions for security. This means you can set specific rules for who can access, read, write, or even delete files and folders on an NTFS drive. This is absolutely crucial for multi-user computers and business environments where data security is a big concern, you know?
FAT32 simply doesn't have these kinds of built-in security features. If you put something on a FAT32 drive, anyone with access to that drive can typically access all the files on it. This makes it less secure for sensitive information, obviously. So, if you're worried about who can get to your stuff, NTFS is definitely the better choice, generally speaking.
Error Recovery and Reliability
NTFS is designed to be much more robust than FAT32. It includes features like a change journal, which can help quickly recover errors if your computer crashes or loses power while writing data. This journal keeps a record of changes made to files and folders, making it easier to restore the file system to a consistent state, which is really helpful, apparently.
FAT32, being an older system, doesn't have these advanced recovery features. If a FAT32 drive gets corrupted, recovering data can be much harder, and you might lose more of your stuff. So, for important data that you can't afford to lose, NTFS offers a higher level of reliability. It's just a bit more forgiving when things go wrong, you know?
Speed and Performance
When it comes to raw speed, the differences between FAT32 and NTFS are often pretty small for everyday tasks, especially on modern computers with fast drives. For very small files, FAT32 might sometimes be slightly quicker due to its simpler structure. However, for larger files and more complex operations, NTFS usually pulls ahead because of its more efficient data organization and caching mechanisms, which is quite useful.
The performance difference is more noticeable when you're dealing with a drive that has many small files or when the drive is nearly full. NTFS tends to handle these situations better, keeping things running more smoothly. But for a simple USB stick moving a few documents, you probably won't notice a huge speed gap between the two, honestly.
When to Pick Which: Use Cases
Choosing the right file system really comes down to what you plan to do with your drive. There's no single "best" option for everyone. It's about matching the file system's strengths to your specific needs, so, you know, think about how you'll use it.
Go With FAT32 If...
You need wide device compatibility: This is FAT32's biggest selling point. If you're going to use your USB drive with various devices like smart TVs, car stereos, older computers, or game consoles, FAT32 is almost always the safest bet. It just works with nearly everything, which is convenient.
Your files are generally small: If you're only storing documents, photos, or music files that are individually less than 4 GB, FAT32 will work just fine. It's perfectly capable for typical everyday storage of smaller items, really.
You're formatting a smaller drive: For USB flash drives under 32 GB, FAT32 is often the default and a perfectly good choice. As My text mentions, there are even tools like Fat32format that help with larger drives if you need to force FAT32 on them for compatibility reasons, you know?
You're not worried about advanced security: If the drive isn't holding sensitive information and you don't need user permissions, FAT32's simpler structure is perfectly adequate. It's just a straightforward way to store things.
Choose NTFS When...
You need to store very large files: If you're dealing with files over 4 GB, such as high-definition videos, large software installations, or disk images, NTFS is your only real option. This is a common need for many users today, so it's a big point, obviously.
You're formatting an internal hard drive or a large external drive for Windows: For your main computer drives or large backup drives that will primarily be used with Windows, NTFS is the standard and recommended choice. It offers the best performance and features for Windows systems, typically.
You need file security and permissions: If you're sharing a computer with others or need to protect certain files from unauthorized access, NTFS's security features are incredibly useful. It adds a layer of protection that FAT32 just doesn't have, which is pretty important.
You want better error recovery: For drives holding important data, NTFS's journaling capabilities provide a safety net against data corruption. It's more reliable in case of unexpected shutdowns or system issues, which is a good thing to have, you know?
Formatting Your Drive: A Quick Guide
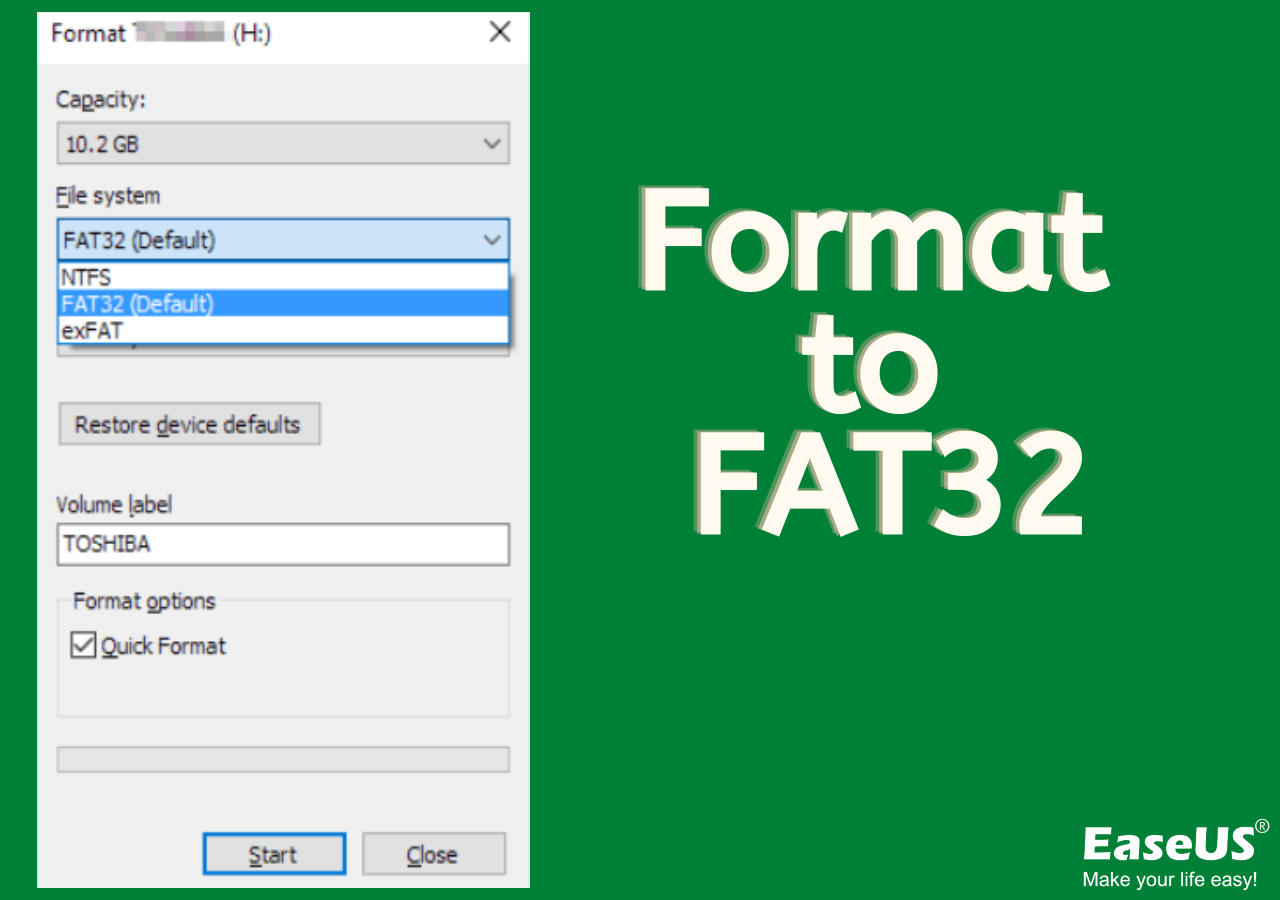
When you're ready to format a drive, the process is pretty straightforward on Windows PCs. You just need to open the File Explorer on your PC, right-click the drive you want to format, and pick "Format." From there, you'll see a list of file systems to choose from. You can then enter a name for the drive, which is a bit like labeling a box.
Formatting to FAT32 on Windows
As my text points out, formatting to FAT32 on Windows 11 or Windows 10 is quite simple. You'll choose FAT32 or exFAT from the file system list. If your drive is larger than 32 GB, Windows' built-in tool might not offer FAT32 as an option. In such cases, you can use a program like Fat32format, which is a free utility that helps you configure any hard drive, micro SD card, SD card, and USB drive that is more than 32 GB to the FAT32 file system. You can learn more about file systems on other tech sites, for example.
There are actually four ways to format USB flash drives to FAT32 on Windows 11/10, plus detailed guides for macOS and Linux users exist. So, it's pretty accessible no matter what system you're using. Converting or formatting a USB flash drive to FAT32 can be done with readily available tools, which is helpful, honestly.
Frequently Asked Questions About File Systems
Is FAT32 better than NTFS?
Neither FAT32 nor NTFS is universally "better"; it really depends on what you need. FAT32 is better for wide device compatibility, especially with older gadgets and game consoles. NTFS is better for modern Windows systems, handling very large files, offering better security, and providing more robust error recovery. So, it's about picking the right tool, you know?
When should I use FAT32 instead of NTFS?
You should use FAT32 when you need your drive to work with many different types of devices, like TVs, car stereos, or game consoles, or if you're only storing files smaller than 4 GB each. It's also a good choice for smaller USB drives where universal compatibility is key. For example, if you're making a bootable drive for an older computer, FAT32 might be the only option that works, apparently.
What is the main difference between FAT32 and NTFS?
The main differences are file size limits, compatibility, and features. FAT32 has a 4 GB single-file limit and works with almost all devices. NTFS supports much larger files and volumes, offers advanced features like file permissions for security and better error recovery, but it's less compatible with non-Windows devices. You can learn more about data storage options on our site, and link to this page here.
When you're looking to decide which file system to use when formatting a disk or USB drive, consider these points. Both have their own set of advantages, and choosing the right one depends on your specific needs. In our increasingly digital world, USB flash drives have become essential tools for data storage and sharing, and picking the right format helps a lot.

FAT32, exFAT et NTFS : Les différences et quel formatage ? - malekal.com
help needed | Speak EV - Electric Car Forums

How to Recover Data from the FAT32 File System on Windows