Repartition Hard Drive: Organize Your Storage Better Today
Have you ever felt like your computer's storage is a bit of a mess, with files scattered everywhere and things just feeling unorganized? Well, you're not alone, you know. Many people find themselves wishing for a tidier way to keep their digital stuff. This feeling of disarray can sometimes make your computer feel slower, or perhaps it just makes finding that one important document a real chore. It's almost like having one giant closet where all your clothes, tools, and books are just piled together.
When we talk about making sense of your computer's storage, a very useful idea comes up: repartitioning your hard drive. This isn't some super technical thing that only computer experts can do, actually. It's really about taking your hard drive, which is basically one big storage space, and dividing it into smaller, more manageable sections. Think of it, in a way, like putting shelves and drawers into that big closet to sort everything out.
This approach, you see, helps with more than just neatness. It can make your computer work a little smoother, keep your important files safer, and even make room for different operating systems if you're into that kind of thing. So, if you're wondering how to get a better handle on your computer's storage, or maybe even improve its performance, learning about repartitioning is a really good place to start. It’s a bit like giving your digital home a proper spring clean, and it can be quite satisfying.
Table of Contents
- What Repartitioning Your Hard Drive Really Means
- Why You Might Want to Repartition Your Drive
- Repartitioning Without Losing Your Important Stuff
- Windows Repartitioning Tools: Built-in and Beyond
- Repartitioning on Other Systems: Mac and Linux
- Partitioning External Hard Drives
- Common Reasons to Repartition Your Hard Drive
- Tips for Optimizing Storage After Partitioning
- Frequently Asked Questions About Repartitioning
- Getting Started with Repartitioning
What Repartitioning Your Hard Drive Really Means
To really get into it, repartitioning a hard drive is basically about taking that one big storage area and splitting it up. You see, a hard drive, when you first get it, is often just one large chunk of space. But you can, in fact, divide it into several distinct sections, or "partitions." Each of these sections then acts like its own separate drive, even though it's all part of the same physical piece of hardware. It's a bit like having a house with several rooms instead of just one enormous open space, which is arguably much more practical.
This process, you know, allows for a much better way to organize and manage all the data you have. Instead of everything being mixed together, you can have a specific section for your operating system, another for your personal documents, perhaps one for games, and so on. This division helps keep things tidy, and it can also make it easier to back up certain types of files without having to copy everything. It's a fundamental concept in managing your computer's storage, and it really helps you take control.
So, when we talk about repartitioning, we're simply referring to changing these divisions after they've already been set up. Maybe you want to make one section bigger, or perhaps you want to create a new one from some unused space. It’s a very flexible way to adapt your storage to your changing needs, which, you know, is something that tends to happen over time as your digital life grows.
Why You Might Want to Repartition Your Drive
There are quite a few good reasons why someone would want to repartition their hard drive, actually. One of the biggest, and perhaps most obvious, is better organization. Imagine having all your work files, personal photos, and system files all jumbled together in one folder; it's a bit chaotic, right? By creating separate partitions, you can keep your operating system on one, your important documents on another, and maybe your entertainment on a third. This makes finding things much simpler, you know, and helps avoid clutter.
Another really strong point for repartitioning is improving performance, at least in some respects. When your operating system has its own dedicated space, it can sometimes run a little more smoothly because it's not constantly competing with other data for read and write access. Also, if one partition gets corrupted, your other partitions might still be safe, which is a pretty big deal for data security. It's a bit like having separate emergency exits for different parts of a building.
For those who like to experiment, or perhaps need different work environments, repartitioning allows you to install multiple operating systems on the same computer. You could have Windows on one partition, and then maybe Linux on another, or even a different version of Windows. This is often called "dual-booting," and it gives you a lot of flexibility without needing two separate computers. So, there are many practical benefits to thinking about how you divide your drive space, really.
Repartitioning Without Losing Your Important Stuff
One of the biggest worries people have when they think about changing their hard drive's layout is losing all their precious data. It’s a very common concern, and a completely understandable one, you know. The good news is that, for the most part, you can absolutely repartition a hard drive without having to wipe everything clean. This is a pretty important aspect, actually, especially for people who have years of photos, documents, and other memories stored on their computers.
Modern tools and techniques have made it much safer to adjust partition sizes or create new ones without touching your existing files. This means you don't necessarily have to go through the lengthy process of backing up everything, then reformatting, and then restoring. That said, it's always, always a really good idea to have a backup of your most important files before you start any major changes to your disk, just in case something unexpected happens. Think of it as a safety net; you hope you don't need it, but you're glad it's there.
Many of the tools we'll talk about are specifically designed to help you rearrange your Windows partitions or create new ones without data loss, which is great news for users of Windows 10 or 11, for example. These tools help you shrink an existing volume to free up space, and then use that free space to create a new partition, all while your original data stays put. It's a really convenient way to manage your storage more effectively, and it gives you peace of mind, too.
Windows Repartitioning Tools: Built-in and Beyond
When it comes to managing your hard drive partitions on a Windows computer, you actually have a couple of main options. There's a tool that comes built right into Windows, which is pretty handy for basic tasks, and then there are also some really powerful third-party programs that offer more advanced features. Knowing which one to use often depends on what you're trying to achieve and how comfortable you are with the process, you know.
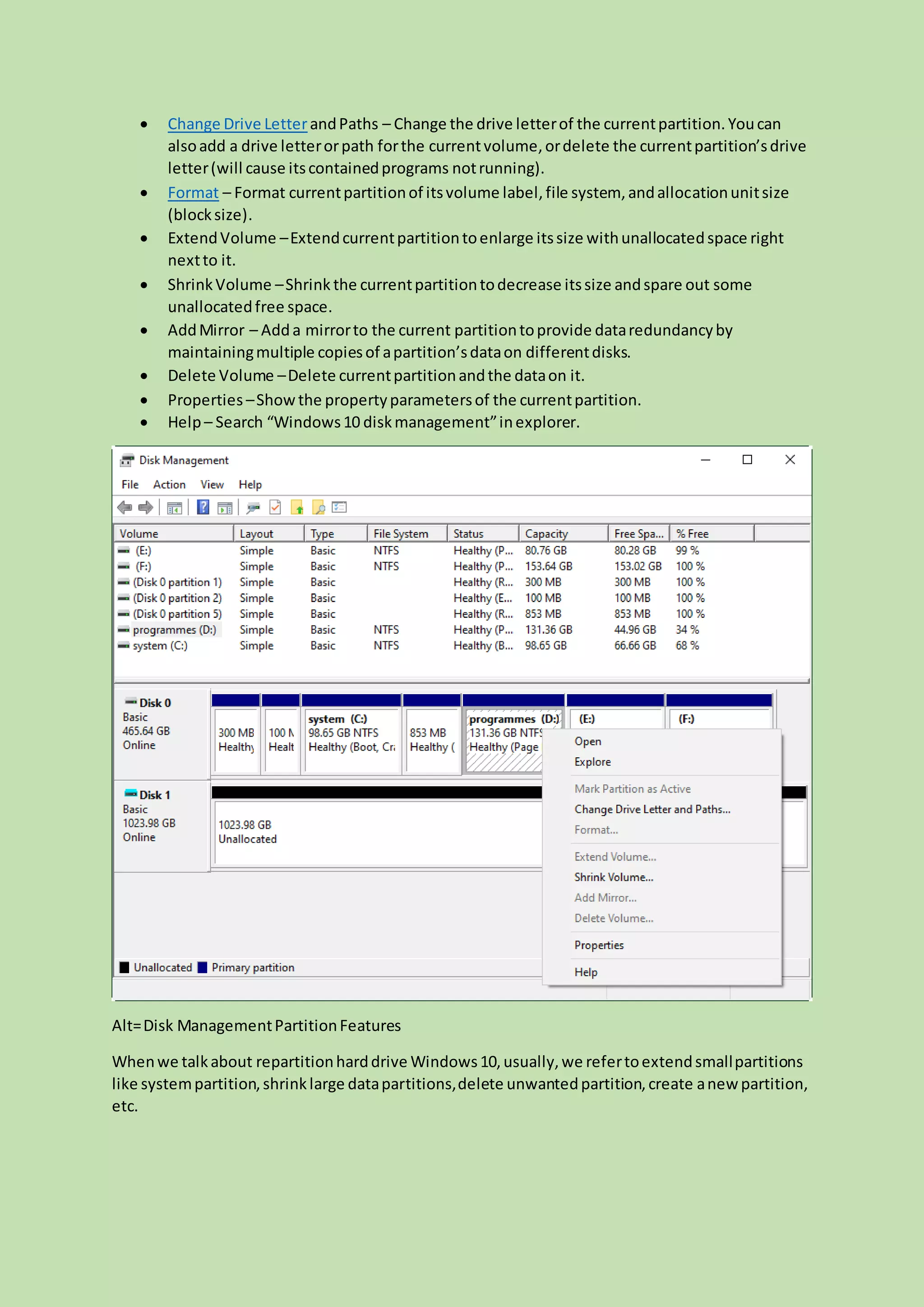
Using Disk Management in Windows
Windows has a feature called Disk Management, which is a fairly straightforward tool for handling your storage. You can find it in Windows 10, Windows 11, and even older versions like Windows 7 and 8. It’s pretty good for common tasks like setting up a new drive, making an existing section smaller, or expanding one. It’s a bit like the basic toolkit you get with a new car; it covers the essentials.
To get started with Disk Management, you typically right-click on the Start button and select "Disk Management." Once it opens, you'll see a visual representation of all your hard drives and their current partitions. If you want to, say, make a partition smaller to create new space, you'd right-click on that partition and choose "Shrink Volume." You then enter how much space you want to take away, and Disk Management does the rest. This creates unallocated space, which you can then use to create a "New Simple Volume," which is basically a new partition. It’s a step-by-step process, so it's not too difficult to follow, actually.
For example, if you have a big C: drive and want to make a separate section for your documents, you could shrink C: to free up some gigabytes. Then, you'd right-click on that new unallocated space and select "New Simple Volume" to create your new partition, giving it a letter like D: or E:. This tool, you know, is quite effective for these kinds of basic tasks, and it generally works without needing to reboot your system for simple changes, which is pretty convenient.
Third-Party Partition Software: MiniTool and Others
While Disk Management is good for the basics, sometimes you need a bit more flexibility or features, you know. That's where third-party partition software really shines. Tools like MiniTool Partition Wizard, AOMEI Partition Assistant, and others offer a wider range of options for managing your hard drive more efficiently. They often come with a more user-friendly interface, too, which can make things a little less intimidating.
These programs, for instance, can do things like merge two smaller partitions into one larger one, split a partition into two, or even convert file systems without losing data. They also frequently have features for optimizing your hard drive's performance, which Disk Management doesn't typically offer. MiniTool, for example, is very popular for its ability to resize partitions, move them around, and even recover lost partitions, all with pretty clear visual guides. It’s a bit like having a specialized set of tools for a more complex job.
Many of these tools, you know, provide free versions that are perfectly capable for most home users. They give you a lot more control over how your storage is organized and how it performs. So, if you're looking to do more than just basic shrinking and creating, exploring options like MiniTool or AOMEI could be a really good idea. They simplify tasks that might otherwise seem quite complex, and they often provide detailed steps on how to achieve your goals without formatting and losing data, which is a major plus.
Repartitioning on Other Systems: Mac and Linux
It's not just Windows users who can benefit from organizing their storage with partitions, actually. People using Macs and those who prefer Linux also have their own ways to divide up their hard drives. The principles are pretty much the same across different operating systems, but the tools and steps you use will, of course, be a little different. It’s important to know the right approach for your specific computer, you know.
Mac: Disk Utility
For Mac users, the built-in tool for managing storage is called Disk Utility. It’s a very capable application that lets you do a lot with your hard drive, including adding, deleting, erasing, or making partitions bigger on your storage devices. You can find it by going to Applications, then Utilities, and then selecting Disk Utility. It’s generally quite user-friendly, with a clean interface that makes it easy to see your drives and their current partitions.
If you want to, say, add a new partition on your Mac, you'd select the drive you want to modify, then click on the "Partition" button. From there, you can use a pie chart-like interface to adjust the size of existing partitions or create new ones from available space. Disk Utility also handles erasing partitions, which can be useful if you're getting rid of old data or preparing a drive for a fresh start. It’s a fairly comprehensive tool for Mac owners to manage their storage effectively, you know.
Linux: Command Line and Graphical Tools
Linux, being a very flexible operating system, offers several ways to partition a hard drive. For those who are comfortable with text commands, the command line provides powerful tools like `fdisk` or `parted`. These tools give you very precise control over every aspect of your disk's layout, but they do require a bit more technical know-how. It's a bit like using a manual camera; you have full control, but you need to understand the settings.
For users who prefer a more visual approach, Linux distributions often come with graphical user interface (GUI) tools for disk management. GParted is a very popular example, and it’s arguably one of the best for managing disk space efficiently on Linux. It lets you resize, move, create, and delete partitions with a mouse, much like the Windows and Mac tools. It's a lot more approachable for those who aren't keen on typing out commands, you know.
These Linux tools are ideal for managing disk space, whether it's on your main internal drive or an external one. They can also often handle various file systems, including those commonly used in Windows (like NTFS) and Mac (like HFS+), in addition to Linux's own file systems like ext4. So, no matter your preference for command line or graphical interfaces, Linux provides robust options for partitioning, which is pretty neat.
Partitioning External Hard Drives
It's not just your computer's internal hard drive that can benefit from being organized into partitions; external hard drives can, too. In fact, partitioning an external drive can be incredibly useful for a variety of reasons, you know. Think about it: you might use an external drive for backups, for transferring files between different computers, or perhaps for storing large media libraries. Having it partitioned can make all these tasks much smoother.
For example, you could create one partition on your external drive specifically for Time Machine backups if you're a Mac user, and another partition for general file storage that's compatible with both Windows and Mac. This way, you don't have to buy multiple external drives for different purposes. It’s a very practical way to get more utility out of a single piece of hardware, which is always a good thing.
The process for partitioning an external hard drive is pretty much the same as for an internal one, using the same tools we've already discussed. So, in Windows, you'd use Disk Management or a third-party tool like MiniTool. On a Mac, you'd use Disk Utility. And on Linux, you'd use GParted or command-line tools. It's a simple yet effective way to organize and optimize your portable storage, too, which can make a big difference in how you manage your data on the go.
Common Reasons to Repartition Your Hard Drive
People repartition their hard drives for a whole bunch of reasons, you know, and these reasons often come down to making their computer life a little easier or more efficient. One very common scenario is when you first get a new computer or a new hard drive. Often, the manufacturer sets it up as one big partition, and you might want to divide it right away for better organization. It’s a bit like moving into a new house and immediately planning where all your furniture will go.
Another frequent reason is to separate your operating system from your personal files. This is a pretty smart move because if your Windows installation ever runs into trouble and you need to reinstall it, you can often do so without affecting your documents, photos, and videos stored on a different partition. This separation offers a kind of safety buffer, which is very reassuring.
Many people also repartition to create space for a second operating system, as we mentioned earlier. This is especially popular among developers, students, or anyone who needs to run specific software that only works on a different OS. Also, sometimes you just need to free up space on a crowded C: drive, and repartitioning allows you to shrink it and allocate that space to a new, more organized section. These are all practical uses that can really improve your computing experience, you know, making things run more smoothly and keeping your data safer.
Tips for Optimizing Storage After Partitioning
Once you've gone through the effort of repartitioning your hard drive, you might be wondering how to really make the most of your new, organized setup. It's not just about dividing the space; it's also about how you use those divisions to keep things running well. Optimizing your storage after partitioning can actually help improve overall performance and keep your data tidy for the long haul, you know.
One key tip is to be consistent with where you save your files. If you've created a "Documents" partition, make sure you're actually saving your documents there, and not accidentally on your C: drive. This consistency helps maintain the organization you worked hard to create. It’s a bit like putting your keys in the same spot every time so you always know where to find them.
Another good practice is to regularly check the free space on each partition. If one partition, say for games, starts getting very full, it might be a good idea to move some older games to an archive partition or an external drive. Keeping a reasonable amount of free space on your system partition (usually C:) is especially important, as Windows needs this space for temporary files and updates to run efficiently. Regularly managing your partitions, perhaps with a tool like MiniTool or AOMEI, can help you keep everything balanced and performing well, you know, ensuring your hard drive stays optimized and your computer feels snappy.
Frequently Asked Questions About Repartitioning
People often have a few common questions when they're thinking about repartitioning their hard drives. It's a process that can seem a little complex at first, so it's natural to seek some clarity, you know. Here are some of the most asked questions.
Can I repartition a hard drive without losing data?
Yes, absolutely, you can often repartition a hard drive without losing any of your existing data. Many modern tools, like Windows Disk Management and third-party software such as MiniTool Partition Wizard, are designed to allow you to shrink, extend, or create new partitions while keeping your files safe. However, it's always, always a really good idea to back up your most important information before you start, just to be on the safe side. It's a bit like wearing a seatbelt; you hope you don't need it, but it's there for protection.
What is the best free software to repartition a hard drive?
For Windows users, there are several excellent free options available. MiniTool Partition Wizard Free Edition and AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard Edition are both very popular choices, actually. They offer a wide range of features beyond what Windows' built-in Disk Management tool provides, including resizing, moving, and merging partitions with a user-friendly interface. For Linux, GParted is a fantastic open-source option that's widely used and very capable. These tools tend to make the process much more approachable, you know.
Why should I partition my hard drive?
There are several compelling reasons to partition your hard drive. Primarily, it helps with better organization, allowing you to separate your operating system, personal files, and applications into distinct sections. This can also lead to improved system performance, as the operating system has dedicated space. Furthermore, partitioning makes it easier to install multiple operating systems (like Windows and Linux) on the same computer, and it can offer a layer of data protection by isolating different types of files. It’s a pretty effective way to manage your storage, you know, making your computer more versatile and easier to maintain.
Getting Started with Repartitioning
So, if you're feeling ready to take charge of your hard drive's organization, repartitioning can be a really rewarding step. Whether you're aiming for a tidier file system, better performance, or the flexibility of multiple operating systems, the tools and knowledge are certainly available. Remember, starting with a backup of your most cherished files is always a wise move, just for that extra peace of mind.
You can begin with Windows' built-in Disk Management for simpler tasks, or perhaps explore a more feature-rich free tool like MiniTool Partition Wizard if you need more advanced options. There are plenty of guides out there, like this comprehensive solution for how to partition hard disk in Windows 11/10/8/7/XP/Vista without formatting, that can walk you through the steps. It’s a process that, while it might seem a bit daunting at first, is actually quite manageable once you get going.
By taking the time to repartition your hard drive, you're not just moving files around; you're actually creating a more efficient and resilient storage system for your digital life. It's a bit like setting up a really good filing system for your office. Learn more about hard drive management on our site, and if you're thinking about other ways to boost your computer, you might want to link to this page about optimizing system startup. With a little planning and the right tools, you can optimize your storage and improve performance effortlessly, which is pretty great, you know.
Easy steps to repartition hard drive in Windows Server 2016.
Repartition hard-drive-windows-10 | PDF
Repartition hard-drive-windows-10 | PDF